General Definition
- IBC (International Building Code – USA)
- The Minimum Required Number of Exits refers to the minimum number of separate and independent means of egress that must be provided on each floor of a building to ensure safe evacuation during an emergency.
- BSL (Building Standards Law – Japan, 建築基準法)
- The Minimum Required Number of Exits under Japan’s Building Standards Law (BSL, Article 21) refers to the mandatory provision of at least two independent exits in buildings that exceed a certain floor area or height to enable safe evacuation.
The minimum number of exits in a building is a critical life safety measure in both IBC (USA) and BSL (Japan). These regulations ensure that occupants have adequate egress options in case of an emergency, reducing the risk of entrapment.
IBC (USA) – Minimum Number of Exits
Under the International Building Code (IBC 2018), the required number of exits depends on occupant load and floor area.
Key Requirements
- Buildings with an Occupant Load of 49 or Less
- Only one exit is required if the space is small enough and travel distances are within limits.
- Buildings with an Occupant Load of 50 or More
- At least two exits are required per floor.
- This applies to most business, assembly, and educational buildings.
- Larger Occupant Loads – Additional Exits Required
- 3 exits are required when the occupant load exceeds 500.
- 4 exits are required when the occupant load exceeds 1,000.
- Exit Separation Distance
- Minimum separation between exits must be at least 1/2 the diagonal of the building (1/3 if sprinklered).
- Travel Distance to Exits
- Maximum travel distance to the nearest exit depends on the occupancy type and fire protection system:
- Unprotected buildings: 200 feet (60 meters).
- Sprinklered buildings: 250-300 feet (75-90 meters).
- Maximum travel distance to the nearest exit depends on the occupancy type and fire protection system:
- Stairwell & Vertical Exit Requirements
- In multi-story buildings, each floor must have at least two independent exit stairways.
BSL (Japan) – Minimum Number of Exits
Japan’s Building Standards Law (BSL, 建築基準法) mandates at least two exits in certain buildings, with specific conditions based on floor area and occupancy type.
Key Requirements
- Business Use Buildings (Office Buildings, etc.)
- At least two exits are required if the floor area exceeds a certain threshold (typically 150m² to 200m² per floor, depending on fire risk).
- Multi-Story Buildings
- At least two stairways are required for floors above a certain height (typically over 31m, about 10 stories).
- High-rises require fireproof staircases.
- Exit Placement & Distance Between Exits
- Exits must be spaced apart to ensure a safe alternative exists in an emergency.
- Minimum exit separation distance is similar to IBC (half the diagonal of the floor plan).
- Emergency Exit Routes & Fireproofing
- Exits must lead to a safe outdoor area or a protected refuge zone in high-rises.
- Certain narrow buildings can have only one exit, provided additional fireproofing measures are in place.
- Underground and Large Public Facilities
- Underground spaces and large public venues must have more than two exits based on floor area and expected occupant load.
Comparison Table: IBC vs. BSL – Minimum Number of Exits
| Feature | IBC (USA) – Required | BSL (Japan) – Required |
| Threshold for Two Exits | Required for occupant load ≥ 50 | Required for office buildings >150-200m² per floor |
| Minimum Exits for High-Rises | 2 for most buildings; 3+ for large occupancy | 2+ required if >31m height (about 10 stories) |
| Separation Between Exits | Min. ½ diagonal distance of the floor (⅓ if sprinklered) | Similar requirement |
| Travel Distance to Exits | 200 ft (unprotected), 250-300 ft (sprinklered) | Similar, but stricter in some cases |
| Underground & Large Public Spaces | More exits required based on size | More exits required based on fire risk & floor area |
Case Study
Minimum Required Exits for a 5-Story Office Building (Group B Occupancy) in the USA vs. Japan
- Project Overview
- A company is constructing a 5-story office building (Group B Occupancy) with a total floor area of 4,500 m² (≈48,500 ft²). The building includes office spaces, meeting rooms, and shared workspaces.
- The project must comply with the International Building Code (IBC – USA) and the Building Standard Law (BSL – Japan) regarding the minimum number of required exits, ensuring a safe and accessible evacuation plan for all occupants, including individuals with disabilities.
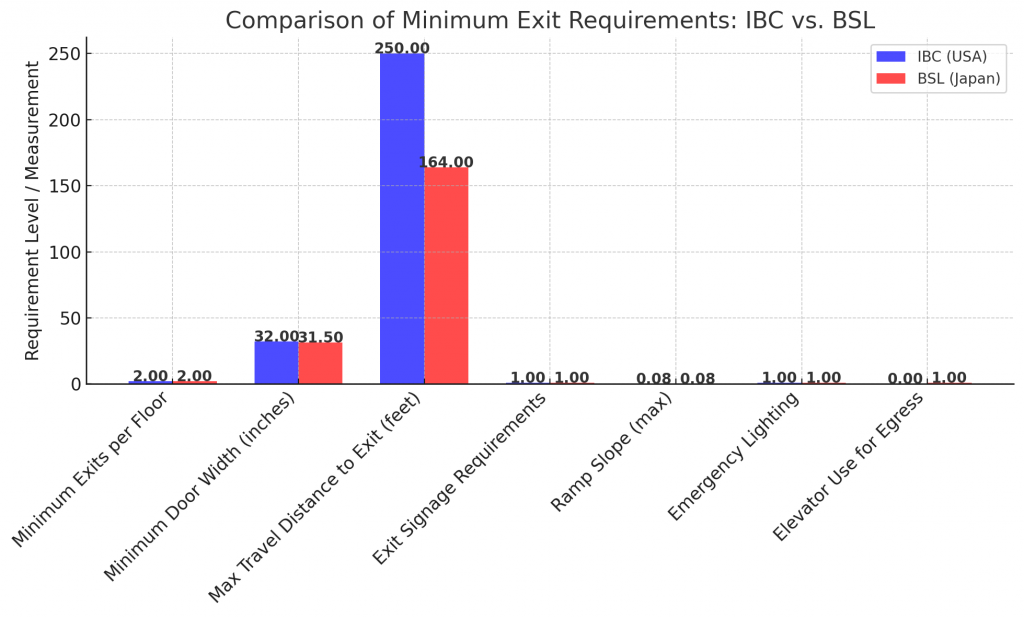
Comparison of Minimum Exit Requirements: IBC vs. BSL
| Category | IBC (USA) – 2018 | BSL (Japan) |
| Minimum Number of Exits per Floor | At least 2 per floor (based on occupant load) | At least 2 per floor for buildings over 500 m² |
| Minimum Door Width for Exiting | 32 inches (81 cm) clear width | 80 cm (31.5 inches) clear width |
| Maximum Travel Distance to Exit | 200 feet (60 m) without sprinklers, 250 feet (75 m) with sprinklers | 50 meters (164 feet) |
| Exit Signage Requirements | Tactile and visual signs required, including Braille | Pictograms and Japanese characters required |
| Ramp Slope (if used in egress) | Max 1:12 (8.33%) | Max 1:12 (8.33%), step-free exits preferred |
| Emergency Lighting | Required along exit routes | Required, must include floor-level lighting for visibility |
| Use of Elevators for Egress | Prohibited (except emergency evacuation elevators) | Certain elevators are permitted for evacuation |
Honolulu (IBC Compliance)
- Design Considerations:
- Two exits per floor are provided to comply with IBC egress requirements.
- Exit doors have a minimum clear width of 32 inches (81 cm) for wheelchair accessibility.
- Maximum travel distance to an exit is 250 feet (75 m) due to sprinkler system installation.
- Tactile, Braille, and illuminated exit signs are installed at every exit and along the evacuation path.
- Emergency lighting is installed along corridors, stairwells, and exit doors to guide evacuees.
- Ramps are provided where necessary, ensuring a maximum slope of 1:12 (8.33%).
- Key Challenges:
- Ensuring that every floor has a compliant second exit, especially in older buildings where retrofitting is necessary.
- Incorporating proper signage that meets ADA requirements for accessibility.
Tokyo (BSL Compliance)
- Design Considerations:
- Two exits per floor are required because the total floor area exceeds 500 m² per story.
- Exit doors have a minimum clear width of 80 cm (31.5 inches).
- Maximum travel distance to an exit is 50 meters (164 feet), requiring strategic placement of exits.
- Pictogram-based signage is installed with Japanese characters for accessibility.
- Emergency lighting includes floor-level markers to enhance visibility for visually impaired individuals.
- Tactile guide blocks (Tenji blocks) are installed near exits to aid visually impaired individuals.
- Some elevators are designated for emergency evacuation and equipped with backup power.
- Key Challenges:
- Meeting the stricter 50-meter maximum travel distance requirement may require additional exits in larger office spaces.
- Integration of emergency evacuation elevators and ensuring power redundancy.
Key Findings:
- Both IBC and BSL require at least two exits per floor, but BSL applies the rule for buildings over 500 m² per story.
- Japan enforces a stricter maximum travel distance to exits (50 m) compared to IBC’s 200-250 feet (60-75 m).
- Japan requires 80 cm (31.5 inches) clear exit doors, while IBC mandates a minimum of 32 inches (81 cm).
- Japan mandates tactile guide blocks at exits, while IBC does not.
- Both IBC and BSL require emergency lighting, but Japan mandates floor-level lighting for better visibility.
- IBC prohibits elevator use in emergencies, while Japan allows emergency-designated elevators for evacuation.
Global Approach
Establishing a cohesive international approach by integrating requirements from the International Building Code (IBC, USA) and Building Standard Law (BSL, Japan), the following unified global recommendations are proposed for Group B occupancy:
- Threshold for Two Exits
- Recommended Global Standard: Two exits are required for occupant loads of 50 or more, or for floor areas exceeding 150-200 m².
- Combines the occupancy-based threshold (IBC) and area-based standard (BSL), ensuring consistency and safety across varying occupancy conditions.
- Minimum Number of Exits for High-Rises
- Buildings up to 31 meters (approx. 10 stories): At least two exits.
- Buildings exceeding 31 meters or high-occupancy: A minimum of three exits, potentially more depending on occupant load and building configuration.
- Integrates both codes, ensuring safe egress in high-rise and high-occupancy buildings.
- Separation Between Exits
- Global Standard: Minimum separation of exits is half the diagonal distance of the building floor area; this can be reduced to one-third if the building is fully sprinklered.
- Provides universal compliance and effective safety measures consistent with both jurisdictions.
- Travel Distance to Exits
- Recommended Global Maximum:
- 200 feet (approximately 61 meters) in buildings without sprinkler systems.
- 250-300 feet (76-91 meters) in fully sprinklered buildings.
- Ensures effective evacuation capability, harmonizing IBC and BSL requirements.
- Recommended Global Maximum:
- Underground & Large Public Spaces
- Additional exits are required based on overall fire risk, occupant load, and floor area.
- Enhanced provisions for exits in underground structures and large public occupancy spaces, accounting for complexity and increased fire risk.
Adopting these globally unified guidelines ensures effective emergency egress, robust occupant safety, and comprehensive international compliance across diverse building scenarios.
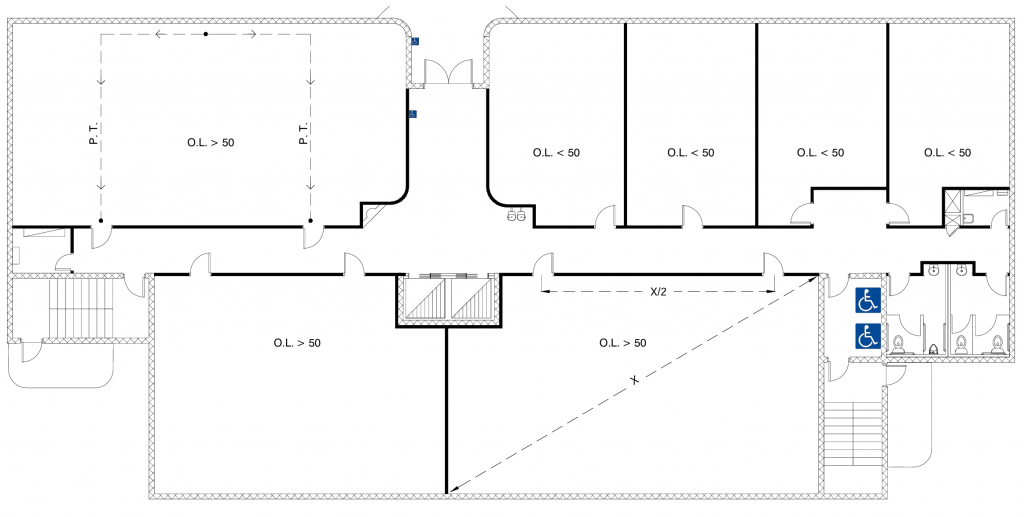
(USA) Max. Path of Travel (P.T.) to an Exit Access = 75 Ft. (21.34 m.) for B Occupancy
(Japan) Exit Doors from a Room must be placed as Far as Possible
(Japan) Two Exit-Stairs Required for a Building where the floor area per Level > 500 sq. m. (5,382 sq. ft.)
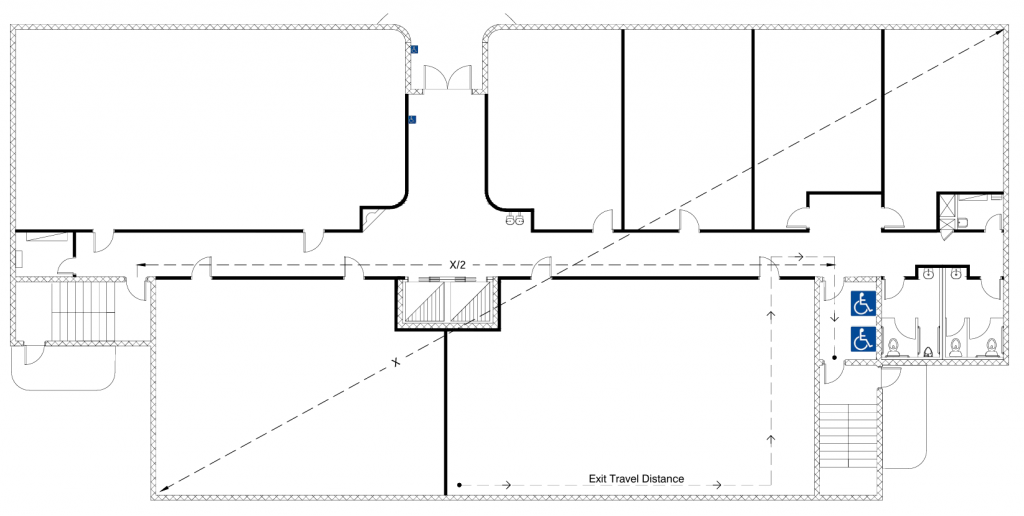
(Japan) Max. Travel Distance to an Exit = 45 m. (148 ft.) w/ F.S., 30 m. (98 ft.) w/ partial F.S., or 22 m. (72 ft.) no F.S.
