General Definitions:
- IBC (International Building Code, USA):
- Specifies fire-resistance requirements for exterior walls based on fire separation distances detailed in Table 602.
- Ratings range from 1-3 hours within 0-10 ft and typically 1 hour within 0-30 ft.
- BSL (Building Standard Law, Japan):
- Articles 2 and 27 require fire-resistant exterior walls specifically in designated fire prevention districts to mitigate fire spread between buildings.
Comparison Table:
| Criterion | IBC (USA) | BSL (Japan) |
| Exterior Wall Fire Rating | 1-3 hours (0-10 ft), typically 1 hour (0-30 ft); dependent on construction type and occupancy | Fire-resistant walls mandated in fire prevention districts; typically 1-2 hours depending on building usage and area density |
| Basis for Rating | Explicitly based on fire separation distance to adjacent structures | Based primarily on location within fire prevention districts and surrounding building density |
| Scope of Application | Clearly defined by distance increments with specific requirements | District-based, broader geographic application without explicit distance increments |
| Materials and Methods | Detailed guidelines for materials and construction methods meeting specified fire ratings | Performance-based criteria emphasizing approved fireproof materials and construction methodologies |
| Compliance and Enforcement | Local authorities enforce strict compliance through inspections referencing Table 602 | National standardized enforcement with certification and periodic inspections |
| Flexibility and Adaptability | Prescriptive standards with limited flexibility due to explicit criteria | Greater flexibility, adapting to regional fire safety needs through district-specific regulations |
| Testing and Certification | Required testing to ASTM E119 or equivalent standards | Required testing based on Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) and other national standards |
Key Differences:
- IBC: Detailed criteria based strictly on building proximity.
- BSL: Regional emphasis on designated districts, less explicit about specific distances but clear about the overall intent for fire prevention.
Case Study:
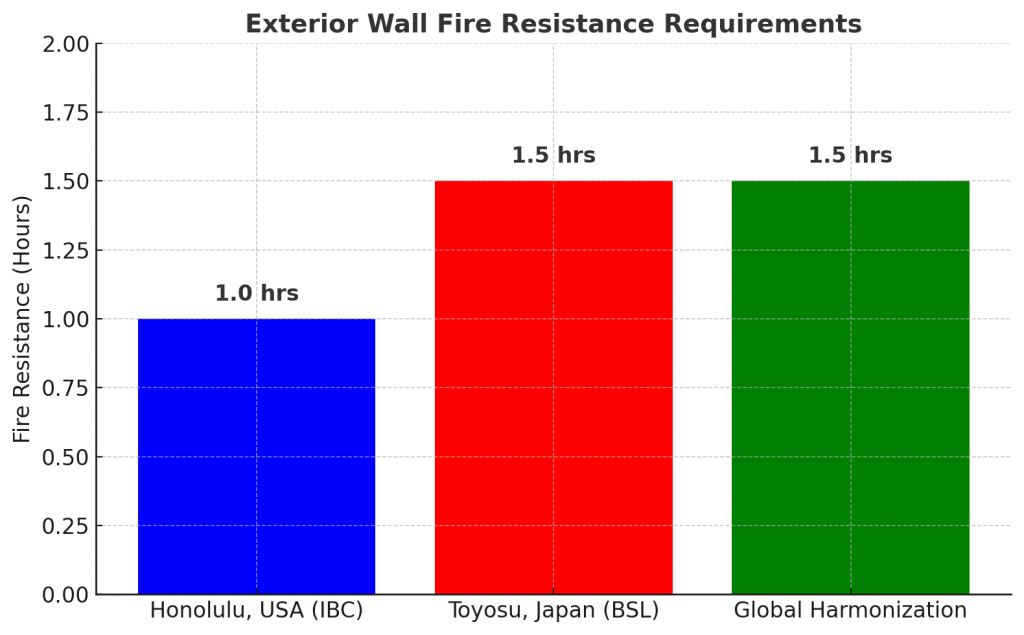
5-Story Office Building
- Honolulu, USA (IBC):
- Exterior Wall Fire Resistance: 1-3 hours based on proximity (typically 1 hour for 10-30 ft separation)
- Toyosu, Japan (BSL):
- Exterior Wall Fire Resistance: Fire-resistant (typically 1-2 hours in fire prevention districts)
Global Approach:
- Unified Exterior Wall Standards:
- Establish globally recognized minimum standards for exterior walls considering both distance and district-specific fire risk criteria.
- Risk and Performance-Based Criteria:
- Create adaptive standards incorporating both distance-based risks (IBC) and location-specific risks (BSL).
- Collaborative Regulatory Framework:
- Implement consistent international testing and certification procedures, facilitating universal compliance and improved global safety standards.
- Continuous International Cooperation:
- Regular international expert forums to address emerging risks, new building technologies, and to harmonize evolving regulations globally.
- Capacity-Building Initiatives:
- Global training and educational programs targeting architects, engineers, and regulatory authorities to ensure effective implementation and understanding of harmonized fire resistance requirements.
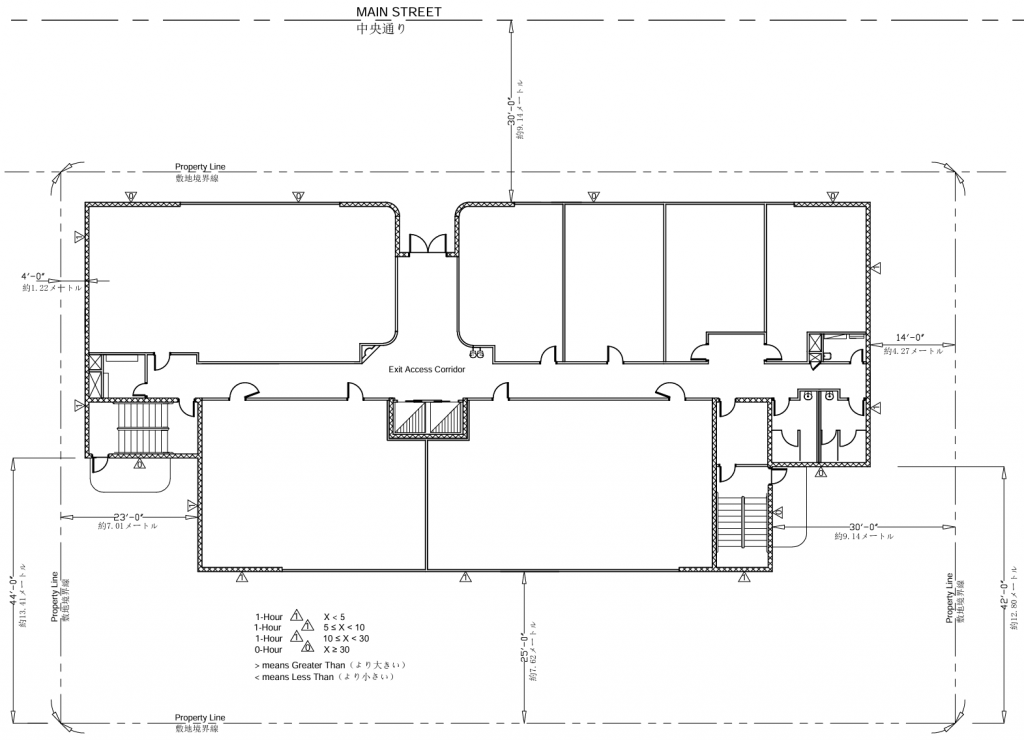
TABLE 602 Fire-Resistance Rating Requirements for Exterior Walls Based on Fire Separation Distance
| Fire Separation Distance (X in feet) | Construction Type | Occupancy Group H | Occupancy Groups F-1, M, S-1 | Occupancy Groups A, B, E, F-2, I, R, S-2, U |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X < 5 | All | 3 hours | 2 hours | 1 hour |
| 5 ≤ X < 10 | Type IA | 3 hours | 2 hours | 1 hour |
| Other types | 2 hours | 1 hour | 1 hour | |
| 10 ≤ X < 30 | Types IA, IB | 2 hours | 1 hour | 1 hour<sup>c</sup> |
| Types IIB, VB | 1 hour | 0 hours | 0 hours | |
| Other types | 1 hour | 1 hour | 1 hour<sup>c</sup> | |
| X ≥ 30 | All | 0 hours | 0 hours | 0 hours |
Notes:
a. Load-bearing exterior walls must also comply with the fire-resistance rating requirements of Table 601.
b. For party walls, refer to Section 706.1.1.
c. Open parking garages that meet Section 406 are not required to have a fire-resistance rating.
d. The fire-resistance rating for an exterior wall depends on both the wall’s fire separation distance and the story where it is located.
e. For special Group H occupancy requirements, see Section 415.6.
f. For special Group S aircraft hangar requirements, see Section 412.3.1.
g. If Table 705.8 allows unlimited unprotected openings in a nonbearing exterior wall, the required fire-resistance rating is 0 hours.
h. For buildings containing only Group U garages or carports, exterior walls do not require a fire rating if the fire separation distance is 5 feet (1523 mm) or more.
i. For Group R-3 buildings of Type IIB or VB construction, exterior walls do not require a fire-resistance rating if the fire separation distance is 5 feet (1523 mm) or more.
表 602 防火区画距離に基づく外壁の耐火性能要件
| 防火区画距離 X(フィート) | 構造の種類 | 用途区分 He | 用途区分 F-1, M, S-1f | 用途区分 A, B, E, F-2, I, Ri, S-2, Uh |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X < 5 (b) | 全て | 3時間 | 2時間 | 1時間 |
| 5 ≤ X < 10 | IA構造 | 3時間 | 2時間 | 1時間 |
| その他の構造 | 2時間 | 1時間 | 1時間 | |
| 10 ≤ X < 30 | IA, IB構造 | 2時間 | 1時間 | 1時間 (c) |
| IIB, VB構造 | 1時間 | 0時間 | 0時間 | |
| その他の構造 | 1時間 | 1時間 | 1時間c | |
| X ≥ 30 | 全て | 0時間 | 0時間 | 0時間 |
注釈:
a. 耐力壁である外壁は、表601の耐火等級要件も満たす必要があります。
b. パーティーウォールの要件については、セクション706.1.1を参照してください。
c. セクション406に適合する開放型立体駐車場は、耐火性能等級は不要です。
d. 外壁の耐火性能等級は、壁の階数および防火区画距離に基づいて決定されます。
e. H用途区分に関する特別要件はセクション415.6を参照してください。
f. G用途区分(航空機格納庫)の特別要件については、セクション412.3.1を参照してください。
g. 表705.8が無制限の開口部を許可する場合、外壁の耐火性能等級は0時間で可。
h. U用途区分のみを含む建物で、専用車庫またはカーポートを有する場合、外壁の防火区画距離が5フィート(1523mm)以上であれば、耐火性能等級は不要です。
