General Definitions:
- IBC (International Building Code, USA):
- Specifies fire resistance ratings based on construction types (Types I, II, III, IV, and V) and occupancy group, incorporating Table 601 and Table 508.4. Ratings typically range from 1-3 hours.
- BSL (Building Standard Law, Japan):
- Requires buildings ≥3 stories or ≥1,000 m² to be classified as fireproof buildings (耐火建築物). Fire resistance standards are prescribed under Articles 2, 27, and 35, mandating structural fireproofing measures based on building height and area.
Comparison Table:
| Criterion | IBC (USA) | BSL (Japan) |
| Basis of Fire Rating | Construction type & occupancy classification detailed in Tables 601 and 508.4 | Based primarily on building size (floor area) and height specified in Articles 2, 27, and 35 |
| Type I & II (Non-combustible Construction) | 2-3 hours typically, depending on occupancy and risk factors (higher for essential facilities) | Buildings ≥3 stories or ≥1,000 m² must meet Fireproof classification, typically requiring 2-3 hours resistance |
| Type III (Combustible/Non-combustible Mixed Construction) | 1-2 hours depending on building occupancy and area limitations | Buildings <1,000 m² or <3 stories generally classified as semi-fireproof, requiring at least 1-2 hours resistance |
| Type IV (Heavy Timber Construction) | Typically 1-2 hours based on building occupancy and risk assessments | Heavy timber construction typically not classified separately; considered under broader fireproof/semi-fireproof standards |
| Type V (Combustible Construction) | Generally 1-hour for smaller, less critical occupancies; higher for larger or more critical occupancies | Combustible construction typically limited by stringent area and height restrictions; usually treated as semi-fireproof requiring at least 1 hour |
| Structural Fireproofing Methods | Specified based on construction materials and methods detailed explicitly in IBC guidelines | Broadly prescribed requirements emphasizing material performance, minimum fire-resistance ratings, and approved testing methods |
| Compliance and Enforcement | Compliance enforced by local authorities with stringent plan checks, inspection processes, and detailed construction documentation | Nationally standardized compliance through inspections, certifications, and documentation consistent across jurisdictions |
Key Differences:
- IBC: Detailed classification system based explicitly on construction type and occupancy. Offers specific guidance per structure type.
- BSL: Broader size-based categorization, emphasizing height and floor area as primary criteria. Less explicit categorization but clear mandates for fireproof status.
Case Study:
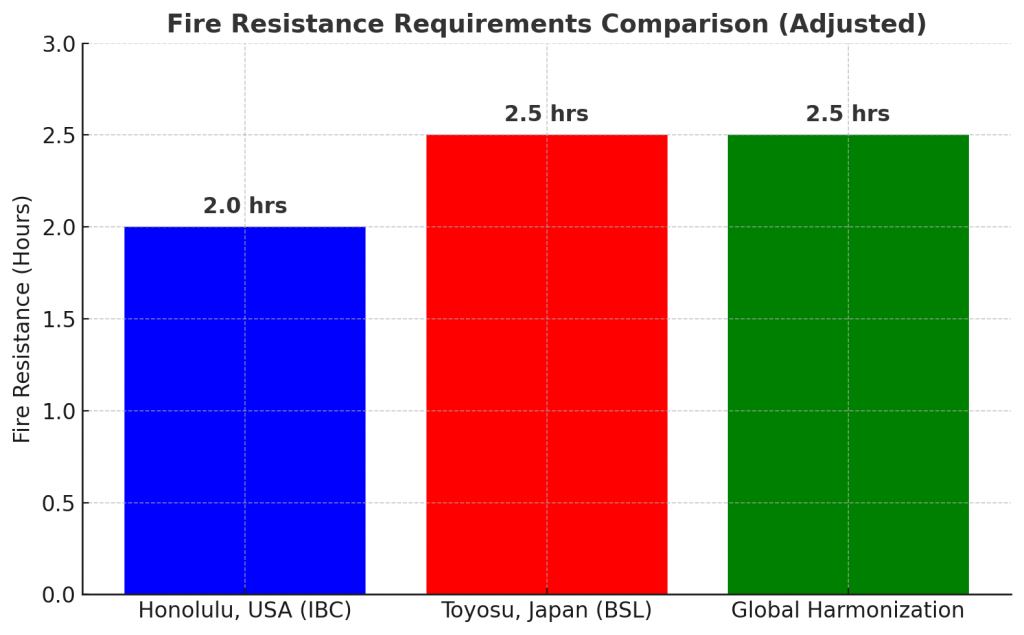
5-Story Office Building (Honolulu, USA vs. Toyosu, Japan):
- Honolulu, USA (IBC):
- Construction Type: Type IIA
- Fire Resistance Required: 2 hours
- Toyosu, Japan (BSL):
- Building Height: 5 stories
- Floor Area: ≥1,000 m²
- Fire Resistance Required: Fireproof Building, typically 2-3 hours
Global Approach:
- Unified Standard Development:
- Establish an internationally recognized set of minimum fire-resistance benchmarks, allowing for universal safety standards that enhance global construction practices.
- Integrated Risk-Based Approach:
- Combine the strengths of the size-based approach (BSL) with the detailed occupancy-based approach (IBC) to develop comprehensive guidelines that assess fire risks effectively in varied scenarios.
- International Collaboration and Information Sharing:
- Promote regular international forums and expert exchanges to facilitate continuous sharing of best practices, innovations in fireproofing technology, and updates in research findings.
- Standardized Testing and Certification:
- Develop universally accepted testing methodologies and certification procedures, ensuring that fire-resistance performance claims are reliable, comparable, and recognized globally.
- Adaptive and Flexible Framework:
- Establish a flexible yet robust framework capable of adjusting to new building technologies, materials, and construction methods to maintain relevance and applicability across different regions and climatic conditions.
Applicable IBC & BSL Standards for “B” Occupancy Fire-Resistance of Structural Elements:
TABLE 601
Fire-Resistance Rating Requirements for Building Elements (in Hours)
| Building Element | Type I A / B | Type II A / B | Type III A / B | Type IV (HT) | Type V A / B |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary structural frame | 3 / 2 (a,b) | 1 / 0 (b) | 1 / 0 (b) | HT | 1 / 0 |
| Bearing walls — Exterior | 3 / 2 | 1 / 0 | 2 / 2 | 2 | 1 / 0 |
| Bearing walls — Interior | 3 (a) / 2 (a) | 1 / 0 | 1 / 0 | 1 / HT | 1 / 0 |
| Nonbearing walls and partitions — Exterior | See to Table 602 for ratings | ||||
| Nonbearing walls and partitions — Interior | 0 / 0 | 0 / 0 | 0 / 0 | See Section 2304.11.2 | 0 / 0 |
| Floor construction and secondary structural members | 2 / 2 | 1 / 0 | 1 / 0 | HT | 1 / 0 |
| Roof construction and secondary structural members | 1½ (b) / 1(b,c) | 1 (b,c) / 0 (c) | 1 (b,c) / 0 | HT | 1 (b,c) / 0 |
Footnotes (Clarifications):
- a. Fire-resistance rating may be reduced by 1 hour when supporting a roof only.
- b. In Group F-1, H, M, and S-1 occupancies, fire protection of structural roof members is not required if:
- The roof is 20 feet or more above any floor below, and
- Fire-retardant-treated wood is used for unprotected members.
- c. In all occupancies complying with Section 2304.11, heavy timber construction may be used where 1-hour or less ratings are allowed.
- d. Interior nonbearing partitions must comply with minimum ratings required by other code sections.
- e. Exterior bearing wall ratings are based on fire separation distances (see Table 602).
- f. For load-bearing elements, fire-resistance ratings follow Section 704.10.
表601:
建築要素の耐火時間要件(時間)
| 建築要素 | タイプ I | タイプ II | タイプ III | タイプ IV | タイプ V | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | A | B | A | B | HT | A | B | |
| 主要構造枠組(f) (§202) | 3 (a,b) | 2 (a,b) | 1(b) | 0 | 1 (b) | 0 | HT | 1(b) | 0 |
| 耐力壁(c,f) | |||||||||
| 外部 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 内部 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1/HT | 1 | 0 |
| 非耐力壁および間仕切り壁 | |||||||||
| 外部 | 表602参照 | ||||||||
| 内部 (d) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | §2304.11.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 床構造および付随する二次構造部材 (§202) | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | HT | 1 | 0 |
| 屋根構造および付随する二次構造部材(§202) | 1½ (b) | 1 (b,c) | 1 (b,c) | 0 (c) | 1 (b,c) | 0 | HT | 1 (b,c) | 0 |
注釈(脚注)
SI単位:1フィート = 304.8mm
(a) 屋根支持部材:主要構造枠組および耐力壁の耐火等級は、屋根の支持のみである場合、1時間
の軽減が認められる。
(b) F-1、H、M、S-1の用途区分を除き、屋根構造の主要構造部材の防火保護は不要。これには、
主要構造枠組、屋根の小梁、および屋根構造が床下20フィート以上である場合が含まれる。耐
火処理木材は使用可能。
(c) すべての用途において、セクション2304.11に準拠する重量木構造(Heavy Timber)は、1
時間以下の耐火等級が求められる場合に許可される。
(d) 他のコードにより規定される耐火等級に従うこと。
(e) 表602で規定される区画壁の耐火等級と同等以上であること。
(f) セクション704.10に示される耐火等級未満ではならない。
