General Definition
- Exit signage and emergency lighting requirements ensure that occupants can safely navigate to exits during normal operations and emergencies, such as fires, power failures, or smoke-filled conditions.
- These systems provide visual guidance, illumination, and reliability in life-threatening situations.
- Both IBC (USA) and BSL (Japan) establish strict regulations for exit sign placement, brightness, emergency lighting coverage, and backup power supply to guarantee safe egress for all building occupants.
- Under IBC 2018, Sections 1013 & 1008.3, exit signage and emergency lighting must be installed in all business occupancies and public buildings to ensure safe evacuation in case of emergencies.
- Under BSL Fire Code Enforcement Regulation, Article 126, Japan’s Building Standards Law (BSL, 建築基準法) establishes mandatory exit signage and emergency lighting requirements in office buildings, commercial spaces, and public-use facilities.
IBC (USA) – Exit Signage & Emergency Lighting Requirements
The International Building Code (IBC 2018, Sections 1013 & 1008.3) outlines mandatory exit signage and emergency lighting requirements for all business occupancies and other public-use buildings.
Key Requirements
- Exit Signage – IBC Section 1013
- Exit signs are required in all occupiable business occupancies and must be visible from any direction of egress travel.
- The word “EXIT” must be illuminated in red or green, with letters at least 6 inches (152 mm) tall and 3/4-inch (19 mm) stroke width.
- Signs must be internally or externally illuminated, with a brightness level of at least 5 foot-candles (54 lux).
- If an exit path is not visible, an illuminated directional sign with an arrow must indicate the exit route.
- Emergency Lighting – IBC Section 1008.3
- Emergency lighting is required in all exit access corridors, stairways, and exit discharge areas.
- Lights must provide at least 1 foot-candle (10.76 lux) at floor level during emergencies.
- The system must remain operational for a minimum of 90 minutes during a power outage using a battery backup or emergency generator.
- Testing & Maintenance Requirements:
- Emergency lighting systems must be tested monthly to ensure proper functionality.
- A full operational test for at least 90 minutes must be conducted annually.
- Additional Requirements for High-Rise & Hazardous Buildings:
- High-rise buildings and hazardous occupancies require redundant backup power sources for emergency lighting.
- Fire-rated corridors must have continuous emergency lighting with automatic activation.
- ADA Compliance for Exit Signs:
- Exit signs must include Braille and tactile characters to assist visually impaired individuals.
- Signs must be installed at consistent heights for accessibility.
BSL (Japan) – Exit Signage & Emergency Lighting Requirements
Japan’s Building Standards Law (BSL, 建築基準法) and Fire Code Enforcement Regulation (Article 126) establish mandatory exit signage and emergency lighting requirements for office buildings, commercial spaces, and public-use facilities.
Key Requirements
- Exit Signage – BSL Fire Code Article 126
- Exit signs are required in all office buildings and large commercial spaces.
- The word “Exit” must be displayed in Japanese (非常口) and English for international compliance.
- Signs must be green with a pictogram of a running figure and an arrow indicating the direction of exit travel.
- Signs must be internally illuminated with a brightness level of at least 10 lux.
- Photoluminescent (glow-in-the-dark) signs are required in buildings where electrical backup may not be available.
- Emergency Lighting – BSL Fire Code Article 126
- Emergency lighting is required in stairwells, hallways, exit routes, and large open areas.
- Lights must provide at least 10 lux (brighter than IBC’s 1 foot-candle) at floor level during emergencies.
- The system must remain operational for at least 30 minutes after a power failure, with battery backup or emergency power supply.
- Fireproof & Smokeproof Egress Considerations:
- Emergency lighting is required to remain functional in smokeproof enclosures and fire-rated stairwells.
- Additional signage must be provided in large atriums or underground spaces to guide evacuees.
- Testing & Maintenance Requirements:
- Emergency lighting systems must be tested every 6 months for functionality.
- Full operational tests must be conducted annually with simulated power failures.
- Barrier-Free & Universal Design Compliance:
- Exit signs must be installed at a height that is visible to all users, including individuals using wheelchairs.
- Tactile indicators and Braille signage are required in public-use facilities and underground buildings.
Comparison Table: IBC vs. BSL
| Feature | IBC (USA) – Required | BSL (Japan) – Required |
| Exit Signs Required In: | All business occupancies | All office buildings |
| Exit Signage Appearance | “EXIT” in red/green, 6-inch text | Green sign with running figure & arrow |
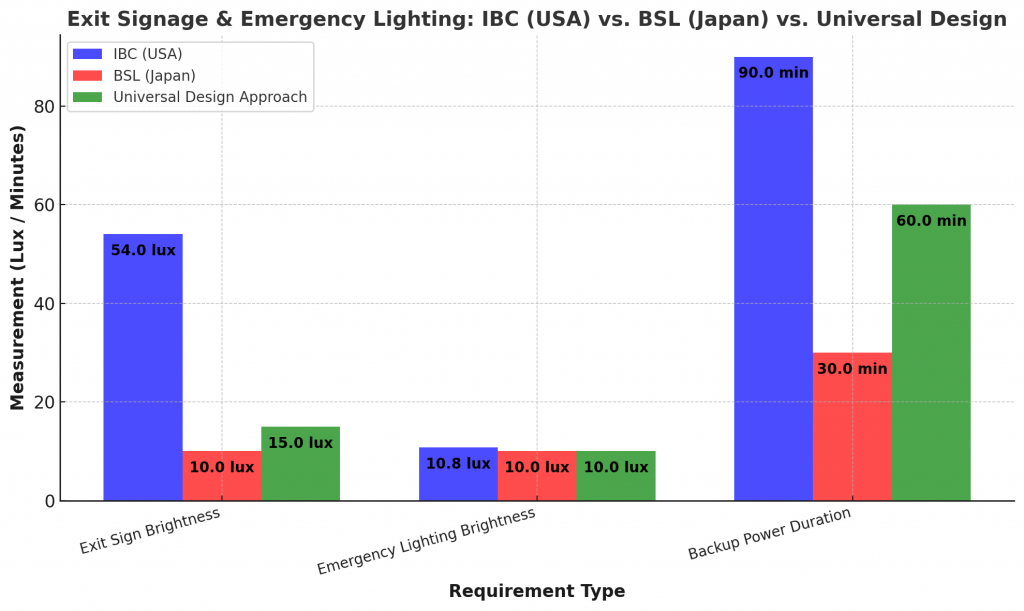
| Minimum Exit Sign Brightness | 5 foot-candles (54 lux) | 10 lux |
| Photoluminescent Exit Signs Allowed? | Yes, in certain areas | Required where backup power may fail |
| Emergency Lighting Required In: | Exit corridors, stairwells, exits | Stairwells, corridors, large open spaces |
| Minimum Emergency Lighting Brightness | 1 foot-candle (10.76 lux) | 10 lux |
| Backup Power Duration | 90 minutes | 30 minutes |
| Testing & Maintenance Frequency | Monthly tests, annual full test | 6-month tests, annual full test |
| ADA / Universal Design Compliance | Braille exit signs required | Tactile indicators required |
Case Study
Exit Signage & Emergency Lighting Compliance – Honolulu vs. Toyosu.
- Project Overview
- A 6-story office building is being designed for:
- Honolulu, USA (IBC jurisdiction)
- Toyosu, Japan (BSL jurisdiction)
- A 6-story office building is being designed for:
- The design team must ensure that the exit signage and emergency lighting systems comply with both IBC (USA) and BSL (Japan) regulations.
Honolulu (IBC) Compliance
- Challenge:
- The initial exit signs were not illuminated internally, which does not comply with IBC’s requirement.
- Emergency lighting needed to remain operational for 90 minutes, requiring battery backup installation.
- Solution:
- Installed illuminated “EXIT” signs with 6-inch lettering and red/green colors.
- Ensured emergency lighting provided at least 1 foot-candle (10.76 lux) at floor level.
- Added backup battery power to maintain emergency lighting for 90 minutes.
Tokyo (BSL) Compliance
- Challenge:
- The original design included red exit signs, which do not comply with Japan’s green running-figure signage standard.
- Emergency lighting only lasted 30 minutes, which meets BSL standards but needed improvements for universal safety.
- Solution:
- Replaced red “EXIT” signs with green pictogram signs (非常口) and directional arrows.
- Ensured exit signs were internally illuminated with at least 10 lux.
- Used photoluminescent exit signs in underground corridors.
- Improved emergency lighting duration from 30 minutes to 60 minutes for additional safety.
Final Universal Design Approach for Both Locations
- To ensure compliance with both IBC (Honolulu) and BSL (Toyosu), the project adopted a universal design strategy:
- Used green pictogram exit signs (非常口) with English text for international readability.
- Increased emergency lighting duration to 60 minutes as a compromise between both codes.
- Ensured photoluminescent exit signs were placed in underground areas for safety.
- Installed tactile exit signage for accessibility in all major exit routes.
Global Approach
To harmonize international standards, combining requirements from the International Building Code (IBC, USA) and Building Standard Law (BSL, Japan), the following comprehensive recommendations are proposed:
Exit Signage
1. Exit Sign Appearance:
- Utilize universally recognized green exit signs featuring the running figure with directional arrows, supplemented by the English text “EXIT” (6-inch letters minimum).
- This ensures international recognition, clarity, and compliance with both IBC and BSL requirements.
2. Minimum Brightness:
- Minimum brightness of 5 foot-candles (approximately 54 lux).
- Achieves brightness levels consistent with IBC (54 lux), surpassing BSL requirements for enhanced visibility.
2. Accessibility and Universal Design:
- Incorporate Braille and tactile indicators for exit signage, ensuring ADA compliance (USA) and barrier-free compliance (Japan).
Emergency Lighting
1. Areas Requiring Emergency Lighting:
- Mandatory in exit corridors, stairwells, and all primary routes of egress. Additionally, include large open assembly spaces.
- Combines the best practices of both IBC and BSL for comprehensive safety.
2. Minimum Emergency Lighting Brightness:
- Establish a global standard of at least 10 lux (approximately 1 foot-candle), consistent with both codes.
2. Minimum Brightness Level:
- Minimum illumination of 10 lux (approximately 1 foot-candle), ensuring adequate visibility per IBC and BSL standards.
3. Backup Power Duration:
- Recommended global minimum duration of 90 minutes for backup power systems (battery/generator), aligning with IBC standards to ensure sufficient evacuation time.
Accessibility and Universal Design Compliance
- Integrate tactile and braille exit signage, complemented by clear, visible exit routes compliant with universal design principles to accommodate diverse users and abilities.
General Recommendations:
- Regular testing and maintenance of exit signage and emergency lighting to ensure reliability, adhering to maintenance standards required by both jurisdictions.
This globally unified approach ensures compliance with international safety standards, providing clarity, safety, accessibility, and effective egress in emergency situations.