General Definition
- Minimum ceiling height requirements establish the lowest allowable height for occupiable spaces in a building.
- These standards ensure adequate headroom, ventilation, safety, and occupant comfort.
- The regulations vary based on building function, occupancy type, and fire safety considerations.
- Both the International Building Code (IBC – USA) and the Building Standards Law (BSL – Japan) specify minimum ceiling heights for different types of spaces, including residential, commercial, and public-use buildings.
IBC (USA) – Minimum Ceiling Height Requirements
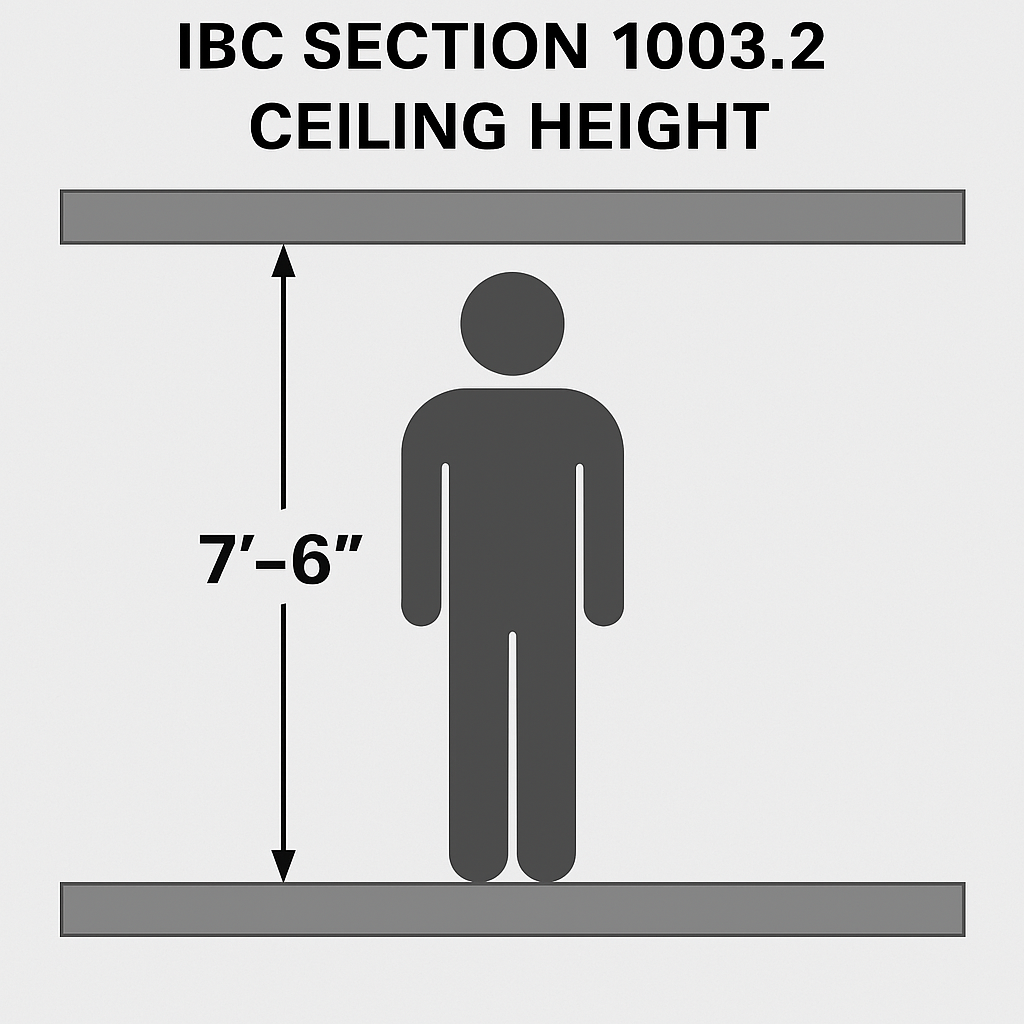
The International Building Code (IBC 2018, Section 1003.2) specifies minimum ceiling height requirements for different types of spaces to ensure comfort, accessibility, and safe egress.
Key Requirements
- General Minimum Ceiling Height:
- 7 feet 6 inches (2286 mm) minimum for all occupiable spaces.
- This includes living areas, offices, and other regularly occupied rooms.
- Exceptions for Certain Spaces:
- Bathrooms, storage rooms, and laundry rooms are allowed to have a minimum ceiling height of 7 feet (2134 mm).
- Corridors and hallways must maintain the 7-foot-6-inch minimum height to avoid obstructions.
- Sloped Ceilings:
- In spaces with sloped ceilings, the required height must be met in at least 50% of the room area.
- The lowest permitted ceiling height is 5 feet (1524 mm) at any point in an occupiable space.
- Headroom Clearance in Stairways:
- Minimum headroom clearance of 80 inches (2032 mm) must be maintained for all stairways and ramps.
- Doorways and exits must also comply with this clearance to ensure safe egress.
- Fire Safety & Accessibility Considerations:
- Dropped ceilings and soffits must not reduce the required clear height in egress paths.
- Ceilings in accessible routes must allow for wheelchair maneuverability and emergency accessibility.
BSL (Japan) – Minimum Ceiling Height Requirements
Japan’s Building Standards Law (BSL, 建築基準法, Article 28) establishes minimum ceiling height requirements based on the function and use of the space.
Key Requirements
- General Minimum Ceiling Height:
- 2.1 meters (6 feet 10 inches) to 2.3 meters (7 feet 6 inches) depending on building function.
- Residential spaces and private rooms often require a minimum of 2.1 m (6 feet 10 inches).
- Larger commercial or office spaces require at least 2.3 m (7 feet 6 inches).
- Ceiling Height for Different Building Types:
- Apartments & small residential units: 2.1 meters (6 feet 10 inches) minimum.
- Office spaces, schools, and commercial buildings: 2.3 meters (7 feet 6 inches) minimum.
- Large public buildings and assembly areas: May require higher ceilings for air circulation and crowd movement.
- Headroom Clearance in Stairways & Corridors:
- Minimum headroom of 2 meters (6 feet 7 inches) in stairways and egress routes.
- This ensures that evacuation routes remain unobstructed and meet barrier-free design standards.
- Fire Safety & Ventilation Considerations:
- Higher ceilings may be required in rooms with limited ventilation to allow for better air circulation and smoke dispersion in case of fire.
- Mechanical ventilation systems must be installed if ceiling heights are lower than 2.3 meters in commercial spaces.
- Barrier-Free & Universal Design Compliance:
- Ceiling height must be sufficient to accommodate mobility aids such as wheelchairs.
- Recessed lighting and ceiling fixtures must not obstruct the minimum clearance requirements.
Comparison Table: IBC vs. BSL
| Feature | IBC (USA) – Required | BSL (Japan) – Required |
| General Minimum Ceiling Height | 7 feet 6 inches (2286 mm) | 2.1 m (6 feet 10 inches) to 2.3 m (7 feet 6 inches), depending on function |
| Minimum Height for Bathrooms, Storage & Utility Rooms | 7 feet (2134 mm) | 2.1 m (6 feet 10 inches) |
| Minimum Stairway & Corridor Headroom | 80 inches (2032 mm) | 2.0 meters (6 feet 7 inches) |
| Sloped Ceiling Allowances | 50% of room must be at 7’6″ | Lower allowances for loft apartments |
| Fire & Ventilation Considerations | Ceilings in fire exits must maintain minimum clearance | Ventilation requirements for low ceilings |
| Barrier-Free & Universal Design Compliance | ADA / ICC A117.1 standards | Barrier-free design for accessible spaces |
Case Study
Ceiling Height Compliance in a Mixed-Use Building – Honolulu vs. Tokyo
- Project Overview
- A 5-story mixed-use building with residential units, office spaces, and retail areas is planned for construction in:
- Honolulu, USA (IBC jurisdiction)
- Toyosu, Japan (BSL jurisdiction)
- A 5-story mixed-use building with residential units, office spaces, and retail areas is planned for construction in:
- The design team must ensure that minimum ceiling heights comply with both IBC (USA) and BSL (Japan) standards while maintaining functional and aesthetic quality.
Honolulu (IBC) Compliance
- Challenge:
- The original design had 7-foot ceilings in office spaces, which did not meet IBC’s 7’6” minimum requirement.
- Solution:
- Increased ceiling height to 7 feet 6 inches (2286 mm) for all office spaces to meet IBC requirements.
- Allowed 7-foot (2134 mm) ceilings in bathrooms and storage rooms per IBC exceptions.
- Ensured 80-inch (2032 mm) clearance in stairways and corridors for safe egress.
Tokyo (BSL) Compliance
- Challenge:
- The original apartment design had 2.1 m (6 feet 10 inches) ceilings, but the commercial office spaces required 2.3 m (7 feet 6 inches) ceilings per BSL.
- Solution:
- Maintained 2.1 m (6 feet 10 inches) ceilings in residential spaces while increasing office ceilings to 2.3 m (7 feet 6 inches).
- Ensured all stairways met the 2.0 m (6 feet 7 inches) minimum clearance for emergency egress.
- Installed mechanical ventilation systems in spaces with lower ceiling heights to comply with fire safety and air circulation requirements.
Final Universal Design Approach for Both Locations
To ensure compliance with both IBC (Honolulu) and BSL (Toyosu), the project adopted a universal design strategy:
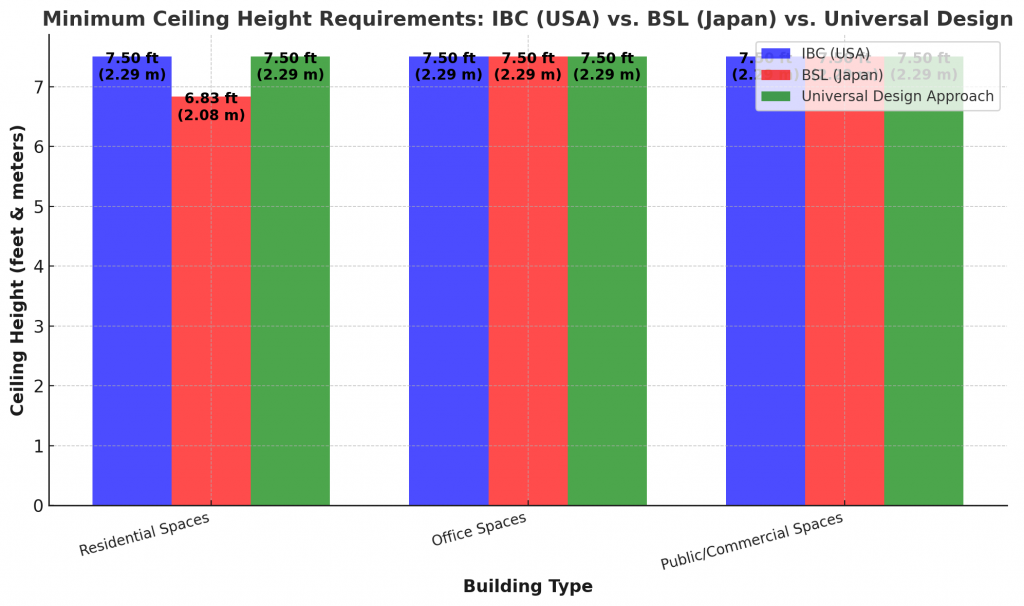
- Standardized all occupied spaces to 2.3 meters (7 feet 6 inches) for a balanced approach that meets both codes.
- Used 2.1-meter ceilings in residential units while maintaining higher ceilings in commercial spaces.
- Incorporated fire-resistant materials and ventilation solutions to meet both fire codes.
- Ensured stairways and corridors provided at least 2.0 meters (6 feet 7 inches) of clearance for safe egress.
Key Takeaways
- IBC requires a minimum ceiling height of 7 feet 6 inches (2286 mm) for most occupied spaces, while BSL allows 2.1 to 2.3 meters (6’10”–7’6”) depending on function.
- BSL has slightly lower ceiling height allowances in residential spaces, while IBC enforces a more standardized approach.
- Universal design strategies balancing both codes help optimize compliance, fire safety, and air circulation requirements.
Global Approach to Ceiling Height for Group B Occupancy
To establish a universally acceptable approach to ceiling heights in Group B occupancy, combining requirements from the International Building Code (IBC, USA) and the Building Standard Law (BSL, Japan), the following unified guidelines are recommended:
- General Minimum Ceiling Height
- Recommended Global Minimum: 7 feet 6 inches (2.3 meters).
- This aligns closely with IBC requirements and meets the upper range of BSL for various functions, ensuring broad compliance and occupant comfort.
- Minimum Ceiling Height for Bathrooms, Storage & Utility Rooms
- Recommended Global Minimum: 7 feet (2.1 meters).
- Matching both the IBC and BSL minimum ensures consistency and practical usability across international projects.
- Minimum Stairway & Corridor Headroom
- Recommended Global Minimum: 80 inches (2.03 meters).
- This accommodates the IBC standard directly and slightly exceeds BSL minimums, enhancing safety and convenience globally.
- Sloped Ceiling Allowances
- At least 50% of the space should maintain the minimum general ceiling height (7 feet 6 inches or 2.3 meters).
- Flexibility to accommodate design variations while ensuring sufficient clearance consistent with IBC guidelines, adjusted for global practicality.
- Fire & Ventilation Considerations
- Ceilings in designated fire exit routes must maintain the minimum headroom clearance of 80 inches (2.03 meters) to ensure unobstructed and safe egress.
- Adequate ventilation measures should be incorporated for spaces with ceiling heights at or near the minimum requirement, as emphasized by the BSL.
- Barrier-Free & Universal Design Compliance
- Spaces must comply with accessibility guidelines consistent with ADA/ICC A117.1 standards (USA) and universal design principles outlined by BSL (Japan).
- This ensures inclusive design facilitating accessibility and usability for all individuals, irrespective of location.
By adopting these integrated global standards, projects can achieve broader regulatory compliance, occupant comfort, safety, and international usability.