General Definition
- IBC (International Building Code – USA)
- Exit width requirements in the International Building Code (IBC) define the minimum width of egress components such as stairs, corridors, doors, and exit routes to ensure safe and efficient evacuation.
- The required width is calculated based on the occupant load, with adjustments for sprinklered buildings and specific occupancy types.
- BSL (Building Standards Law – Japan, 建築基準法)
- Exit width requirements in Japan’s Building Standards Law (BSL, Article 119) establish fixed minimum widths for exit routes, staircases, and corridors in buildings based on their use and size rather than occupant load calculations.
Exit width requirements ensure that building occupants can safely and efficiently evacuate during an emergency. Both IBC (USA) and BSL (Japan) regulate minimum exit widths based on the number of occupants, type of egress component, and overall building use.
IBC (USA) – Exit Width Requirements
Key Requirements:
- Exit Width Calculation Based on Occupant Load
- Stairways: Minimum 0.3 inches (7.62 mm) per occupant in non-sprinklered buildings.
- Stairways: Minimum 0.2 inches (5.08 mm) per occupant in fully sprinklered buildings.
- Other Egress Components (e.g., corridors, doors): Minimum 0.2 inches (5.08 mm) per occupant in non-sprinklered buildings.
- Other Egress Components: Minimum 0.15 inches (3.81 mm) per occupant in fully sprinklered buildings.
- Minimum Egress Widths
- Stairs must be at least 44 inches (1118 mm) wide if serving 50 or more occupants.
- Corridors and exit routes must be at least 36 inches (915 mm) wide.
- Doors providing egress must be at least 32 inches (813 mm) clear width when open.
- Exceptions for Small Occupant Loads
- Stairs serving less than 50 occupants may be 36 inches (914 mm) wide instead of 44 inches.
- Wider Staircases for High Occupant Loads
- Large assembly spaces (e.g., theaters, stadiums) may require extra-wide staircases and exits.
- Sprinklered Buildings Have Reduced Requirements
- If the building is fully sprinklered, exit width requirements are reduced, as fire suppression lowers the evacuation risk.
BSL (Japan) – Exit Width Requirements
Building Standards Law (BSL) Article 119. Japan’s Building Standards Law (BSL, 建築基準法) sets fixed minimum exit width requirements based on building type and occupancy.
Key Requirements:
- Minimum Exit Route Width
- 90 cm (35.4 inches) is the minimum required width for exit routes in standard buildings.
- Minimum Stair Widths in Large Office Buildings
- 120 cm (47.2 inches) is the minimum required width for staircases in large office buildings.
- Fireproof Buildings May Require Wider Exits
- In some cases, stair width may increase to 140 cm (55.1 inches) in high-occupancy buildings.
- BSL Uses Fixed Widths Instead of Occupant-Based Calculations
- Unlike IBC, BSL does not adjust exit width based on the number of occupants in a linear calculation.
- Instead, BSL categorizes buildings and applies fixed width requirements.
Comparison Table: IBC vs. BSL – Exit Width Requirements
| Feature | IBC (USA) – Occupant-Based Calculation | BSL (Japan) – Fixed Minimum Widths |
| Exit Width for Stairs | 0.3 inches (7.62 mm) per occupant (non-sprinklered) 0.2 inches (5.08 mm) per occupant (sprinklered) | 120 cm (47.2 inches) for large office buildings |
| Exit Width for Corridors | 0.2 inches (5.08 mm) per occupant (non-sprinklered) 0.15 inches (3.81 mm) per occupant (sprinklered) | 90 cm (35.4 inches) minimum width |
| Minimum Door Width | 32 inches (813 mm) | BSL does not specify door width separately |
| High-Occupancy Buildings | Stair widths increase based on occupant load | Stair width increases to 140 cm (55.1 inches) in large buildings |
| Sprinklered Building Adjustments | Lower width requirements allowed | No adjustment based on sprinkler system |
Case Study
Exit Width Requirements for a 5-Story Office Building – Honolulu vs. Tokyo
- Project Overview
- A company is constructing a 5-story office building (Group B Occupancy) with a total floor area of 4,500 m² (≈48,500 ft²). The building consists of:
- Office spaces, meeting rooms, and shared workspaces
- Two stairwells serving all floors
- Multiple corridors leading to exit doors
The project must comply with International Building Code (IBC – Honolulu, USA) and Building Standards Law (BSL – Tokyo, Japan) regarding exit width requirements, ensuring safe and accessible evacuation for all occupants, including individuals with disabilities.
IBC 2018, Sections 1005.3.1 & 1005.3.2
Exit width in IBC is determined based on occupant load and type of egress component (e.g., stairs vs. corridors).
- Step 1: Calculate Occupant Load (Per Floor)
- The office space occupant load factor is 1 person per 100 ft² (9.3 m²).
- Each floor = 900 m² (9,687 ft²)
- Occupant load per floor = 900 m² ÷ 9.3 m²/person ≈ 97 occupants
- Total building occupant load (5 floors) = 5 × 97 = 485 occupants
- Step 2: Calculate Exit Width Based on Occupant Load
- Stairways (IBC 1005.3.1)
- Minimum required width = 0.2 inches (5.08 mm) per occupant (sprinklered building)
- 485 occupants × 0.2 inches = 97 inches (2,464 mm) total stair width required
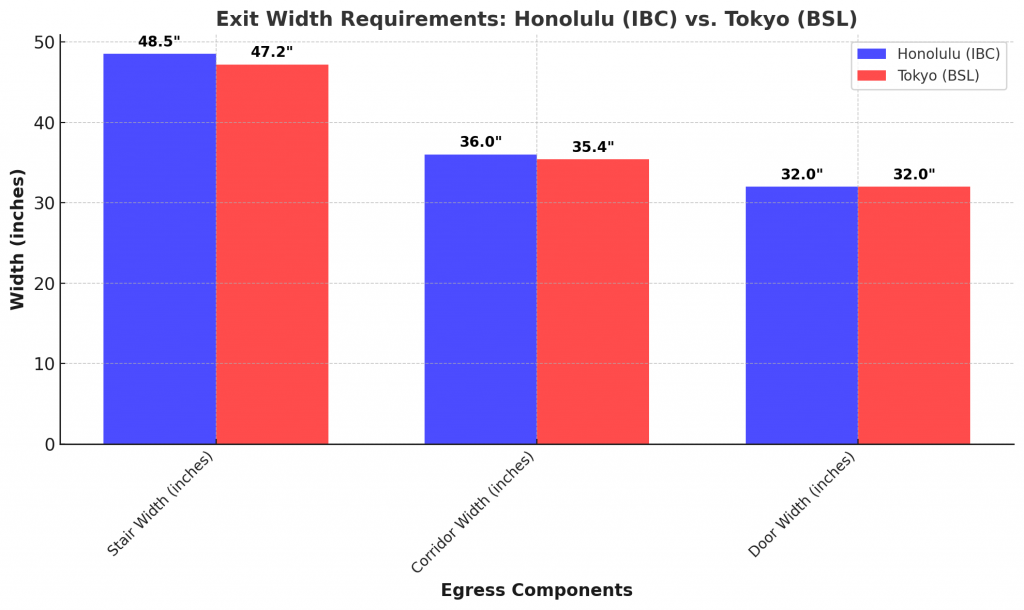
- Since there are two stairwells, each must be at least 48.5 inches (1,232 mm) wide.
- Stairways (IBC 1005.3.1)
- Corridors & Doors (IBC 1005.3.2)
- Corridor width minimum = 0.15 inches (3.81 mm) per occupant
- 485 occupants × 0.15 inches = 72.75 inches (1,848 mm) total corridor width required
- Minimum corridor width per IBC = 36 inches (915 mm), but design should allow for wider corridors for efficiency.
- Doors must provide a minimum clear opening of 32 inches (813 mm).
Honolulu (IBC) Compliance Challenges & Solutions
The original design had 44-inch-wide staircases, which did not meet the 48.5-inch requirement.
The final design increased stair width to 50 inches (1,270 mm) per stairwell.
Corridors were expanded to 48 inches (1,220 mm) for improved accessibility.
Building Standards Law (BSL) Article 119
Exit width in BSL (Japan) is based on fixed minimum widths rather than occupant load calculations.
- Stairways:
- For large office buildings, stairways must be at least 120 cm (47.2 inches) wide.
- High-occupancy buildings may require stair widths of 140 cm (55.1 inches).
- Since this is a 5-story office building, 120 cm (47.2 inches) is required for each stairwell.
- Corridors & Exit Routes
- Corridors must be at least 90 cm (35.4 inches) wide.
- Wider corridors are encouraged for high-traffic areas.
Tokyo (BSL) Compliance Challenges & Solutions
The original design used 44-inch-wide stairs (IBC-compliant), but this was below BSL’s 120 cm (47.2 inches) requirement.
The final design increased stair width to 120 cm (47.2 inches) per stairwell.
Corridors were expanded to 100 cm (39.4 inches) for universal accessibility.
Final Universal Design Approach for Both Locations
To ensure compliance with both Honolulu (IBC, USA) and Tokyo (BSL, Japan), the project adopted a universal approach:
- Standardized stair width at 120 cm (47.2 inches) for both Honolulu and Tokyo.
- Designed corridors at 100 cm (39.4 inches) wide, exceeding both minimums.
- Used 32-inch-wide doors (813 mm) for consistency between jurisdictions.
- Ensured all stairwells had handrails, tactile warning strips, and visual signage for accessibility.
Comparison of Final Exit Widths for Both Locations
| Egress Component | Honolulu (IBC, USA) Requirement | Tokyo (BSL, Japan) Requirement | Final Universal Design Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stair Width | 48.5 inches (1,232 mm) | 120 cm (47.2 inches) | 120 cm (47.2 inches) |
| Corridor Width | 36 inches (915 mm) minimum | 90 cm (35.4 inches) minimum | 100 cm (39.4 inches) |
| Door Width | 32 inches (813 mm) | Not separately specified | 32 inches (813 mm) |
Key Takeaways
- IBC (Honolulu) calculates exit width based on occupant load, while BSL (Tokyo) applies fixed width standards based on building type and size.
- BSL mandates a minimum stair width of 120 cm (47.2 inches) for office buildings, while IBC stair width can be as low as 48.5 inches (1,232 mm) based on calculations.
- A universal design approach exceeding both requirements ensures a safer, internationally compliant building design for both Honolulu and Tokyo.
Global Approach
To harmonize and simplify exit width requirements internationally, incorporating elements of both the International Building Code (IBC, USA) and the Building Standard Law (BSL, Japan), the following global recommendations for Group B occupancy are provided:
- Exit Width for Stairs
- Recommended Global Standard: 0.2 inches (5.08 mm) per occupant (sprinklered buildings)
- Alternate (Non-Sprinklered Buildings): 0.3 inches (7.62 mm) per occupant
- Minimum width: 44 inches (1120 mm)
- Utilizing occupant-based measurements from the IBC provides flexibility and scales with occupancy, while the minimum complies with practical use aligned closely with BSL guidance.
- Exit Width for Corridors
- Recommended Global Standard: 0.15 inches (3.81 mm) per occupant (sprinklered buildings), with a minimum corridor width of 90 cm (35.4 inches).
- Non-sprinklered buildings: 0.2 inches (5.08 mm) per occupant with the same minimum width.
- These dimensions meet practical safety requirements of both IBC and BSL, ensuring efficient egress under diverse conditions.
- Minimum Door Width
- Recommended Global Minimum: 32 inches (813 mm)
- Addresses explicit IBC standards and universally promotes safe and efficient movement of occupants.
- Recommended Global Minimum: 32 inches (813 mm)
- Adjustments for Sprinklered vs. Non-Sprinklered Buildings
- Utilize lower occupant-based exit width requirements for sprinklered buildings to encourage and recognize enhanced fire safety provisions.
- Non-sprinklered buildings must comply with stricter width requirements to ensure sufficient safety margins.
- Universal Accessibility & Barrier-Free Design
- Incorporate universal accessibility principles as per ADA/ICC A117.1 (USA) and ensure compliance with Japanese barrier-free design standards, guaranteeing equitable egress access.
- Door Width and Accessibility
- Minimum door widths should adhere explicitly to the ADA guidelines of 32 inches (813 mm) clear width.
- Even though the BSL does not explicitly specify door widths, adhering to ADA guidelines ensures global accessibility compliance.
These globally harmonized recommendations provide clarity, flexibility, and comprehensive safety in egress design, balancing practicality, international compliance, occupant safety, and accessibility.
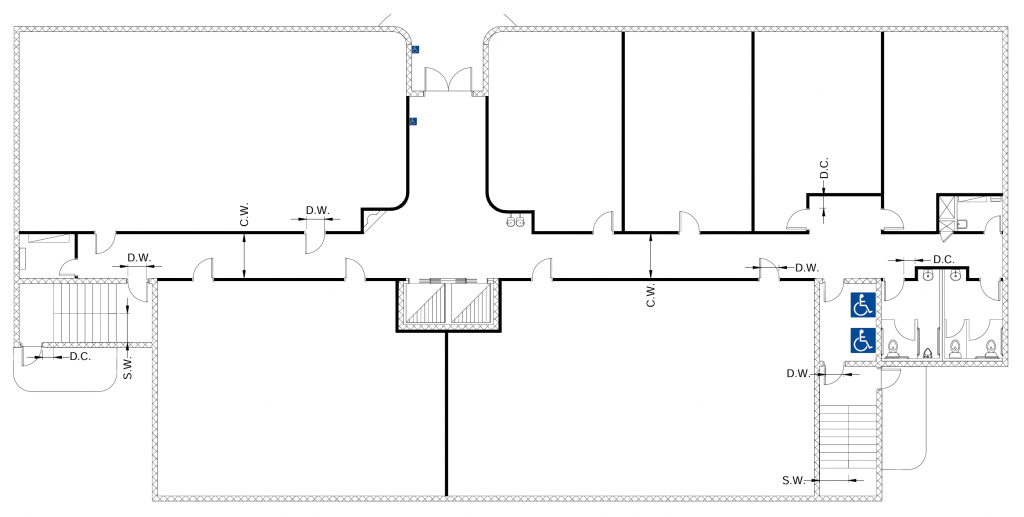
USA: C.W. 44 in. (112 cm.) * S.W. 48 in. (122 cm.) * D.W. 32 in (81 cm.) * D.C. 24 in. (61 cm.)
Japan: C.W. 60 cm. (63 in.) * S.W 120 cm. (47.2 in.) D.W. 80 cm. (31.5 in.) D.C. 40 cm. (15.75 in.)
