General Definition
- Exiting door requirements define the minimum dimensions, swing direction, and operational standards for doors used in emergency egress routes.
- These regulations ensure that occupants can safely evacuate during emergencies without obstruction, congestion, or mechanical failure.
- Both the International Building Code (IBC – USA) and the Building Standards Law (BSL – Japan) establish mandatory minimum width, height, and hardware requirements for exit doors, considering fire safety, accessibility, and evacuation efficiency.
- Under IBC 2018, Sections 1010.1.1 & 1010.1.2.1, exit doors must provide safe and unobstructed egress for business occupancies, residential buildings, and public-use facilities.
- Under BSL Article 119 & Fire Safety Regulations, exit doors must ensure safe passage, fire containment, and accessibility in office buildings, commercial spaces, and high-rise buildings.
Exit doors are essential components of a building’s egress system, ensuring that occupants can safely evacuate during emergencies.
IBC (USA) – Exiting Door Requirements
The International Building Code (IBC 2018, Sections 1010.1.1 & 1010.1.2.1) mandates that exit doors provide a safe, unobstructed means of egress, with minimum width, swing direction, and operational requirements.
Key Requirements
- Minimum Clear Width for Exit Doors – IBC 1010.1.1
- Exit doors must provide at least 32 inches (813 mm) of clear width.
- This ensures that wheelchairs, stretchers, and large groups of occupants can pass through safely.
- The clear width is measured when the door is fully open at 90 degrees, ensuring unobstructed passage.
- Minimum Door Height – IBC 1010.1.2
- Exit doors must have a minimum height of 80 inches (2032 mm) to accommodate all occupants, including individuals using mobility aids.
- This requirement applies to all occupancies, including business, residential, and public-use buildings.
- Swing Direction of Exit Doors – IBC 1010.1.2.1
- Exit doors must swing in the direction of egress travel if serving an occupant load greater than 50.
- This prevents bottlenecking during evacuation, ensuring doors do not block escape routes when opened.
- Exceptions:
- Small rooms with an occupant load of 50 or fewer may have doors that swing inward.
- Certain security-controlled egress doors may use fail-safe unlocking mechanisms.
- Hardware & Locking Requirements – IBC 1010.1.9
- Exit doors must be operable without the use of a key, special knowledge, or force.
- Panic hardware or fire exit hardware is required for doors in assembly, educational, and high-occupancy business buildings.
- Delayed egress locks are allowed in specific cases but must disengage upon activation of the fire alarm.
- Automatic & Power-Operated Doors – IBC 1010.1.4.1
- Automatic sliding doors must comply with accessibility standards and be designed for fail-safe operation during power failures.
BSL (Japan) – Exiting Door Requirements
Japan’s Building Standards Law (BSL, 建築基準法, Article 119) establishes clear width, swing direction, and fire safety requirements for exit doors in office buildings, commercial spaces, and high-rise buildings.
Key Requirements
- Minimum Clear Width for Exit Doors
- Exit doors must provide at least 80 cm (31.5 inches) of clear width.
- This allows for safe passage of wheelchairs, mobility aids, and evacuees.
- Certain large commercial buildings may require wider doors, especially in areas with high occupant loads.
- Minimum Door Height
- Exit doors must have a minimum height of 200 cm (78.7 inches).
- This is slightly lower than IBC’s 80-inch (2032 mm) requirement but still ensures comfortable egress for most occupants.
- Swing Direction of Exit Doors – Fire Safety Regulations
- Exit doors must swing outward in large office buildings and public-use facilities.
- This prevents doors from blocking egress routes or creating congestion during an emergency.
- Certain small rooms (low occupancy) may have doors that swing inward, but these must not obstruct escape paths.
- Hardware & Locking Requirements
- Exit doors must be operable from the inside without the use of a key or special tools.
- Panic bars or emergency release mechanisms are required in high-occupancy buildings.
- Self-closing and automatic fire-rated doors are required for enclosed stairwells and smokeproof exits.
- Sliding Doors & Automatic Exit Systems
- Automatic sliding doors are permitted in commercial buildings but must open manually in case of a power failure.
- Barrier-free requirements apply, ensuring that automated exit doors remain accessible to individuals with disabilities.
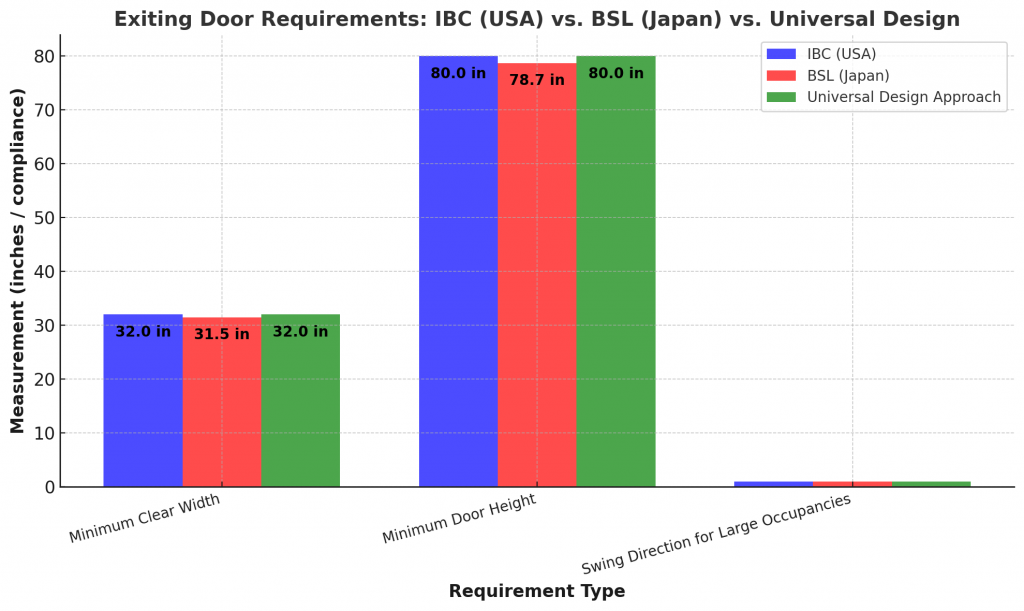
Comparison Table: IBC vs. BSL
| Feature | IBC (USA) – Required | BSL (Japan) – Required |
| Minimum Clear Width | 32 inches (813 mm) | 80 cm (31.5 inches) |
| Minimum Door Height | 80 inches (2032 mm) | 200 cm (78.7 inches) |
| Swing Direction for Large Occupancies | Outward for >50 occupants | Outward for large office buildings |
| Self-Closing & Fire-Rated Doors | Required in stairwells & fire exits | Required in stairwells & fire exits |
| Panic Hardware / Emergency Release | Required in high-occupancy buildings | Required in high-occupancy buildings |
| Automatic Doors Allowed? | Yes, with fail-safe manual override | Yes, must open manually in emergencies |
| Barrier-Free & Universal Design Compliance | ADA / ICC A117.1 standards | Barrier-free design for accessibility |
Case Study
Exiting Door Compliance – Honolulu vs. Toyosu
- Project Overview
- A 10-story office building is being designed for:
- Honolulu, USA (IBC jurisdiction)
- Toyosu, Japan (BSL jurisdiction)
- A 10-story office building is being designed for:
- The design team must ensure that exit doors comply with both IBC (USA) and BSL (Japan) regulations.
Honolulu (IBC) Compliance
- Challenge:
- The original design had 30-inch-wide (762 mm) exit doors, which do not meet IBC’s 32-inch (813 mm) requirement.
- Certain conference room doors swung inward, which is not permitted for occupant loads greater than 50.
- Solution:
- Increased exit door width to 32 inches (813 mm) to comply with IBC.
- Ensured all doors serving >50 occupants swing outward for emergency egress.
- Installed panic hardware on assembly and business occupancy exit doors.
Tokyo (BSL) Compliance
- Challenge:
- The original door width was 75 cm (29.5 inches), which does not meet BSL’s 80 cm (31.5 inches) requirement.
- Certain doors swung inward in high-occupancy areas, which violates BSL’s requirement for outward-swinging doors in large office buildings.
- Solution:
- Increased exit door width to 80 cm (31.5 inches) per BSL regulations.
- Ensured doors in large office buildings swing outward to comply with fire safety regulations.
- Installed self-closing, fire-rated doors in enclosed stairwells.
Final Universal Design Approach for Both Locations
To ensure compliance with both IBC (Honolulu) and BSL (Tokyo), the project adopted a universal design strategy:
- Standardized all exit doors at 32 inches (813 mm) wide, exceeding BSL’s 80 cm requirement.
- Ensured all high-occupancy spaces had outward-swinging doors, meeting both IBC and BSL regulations.
- Installed panic hardware and automatic door closers to improve safety and accessibility.
- Integrated fail-safe manual override systems in automatic sliding doors for universal compliance.
Key Takeaways
- IBC requires a 32-inch (813 mm) minimum exit door width, while BSL requires 80 cm (31.5 inches).
- Both codes require outward-swinging doors for high-occupancy spaces to ensure safe egress.
- Panic hardware is required in high-occupancy buildings under both IBC and BSL.
- A universal design approach with a 32-inch door width and outward-swinging doors ensures compliance with both codes.
Global Approach
To establish unified international door standards for Group B occupancy, synthesizing requirements from the International Building Code (IBC, USA) and the Building Standard Law (BSL, Japan), the following global recommendations are proposed:
Minimum Clear Width
- Recommended Global Minimum: 32 inches (813 mm)
- Ensures compliance with ADA accessibility standards (IBC) and exceeds BSL minimums for improved occupant comfort and accessibility.
- Minimum Door Height
- Recommended Global Minimum: 80 inches (2032 mm)
- Aligns precisely with IBC requirements and slightly exceeds BSL standards, offering universal suitability and comfortable clearance.
- Swing Direction for Large Occupancies
- Global Standard: Doors must swing outward for occupancy greater than 50 persons or in large office buildings.
- Harmonizes both codes, promoting efficient and safe emergency egress.
- Self-Closing & Fire-Rated Doors
- Mandatory Requirement: Install self-closing, fire-rated doors in stairwells, fire exits, and areas designated for fire compartmentation.
- Consistent across both standards, ensuring reliable performance and enhanced fire safety internationally.
- Panic Hardware & Emergency Release
- Required Globally: Panic hardware or emergency release mechanisms must be installed in high-occupancy buildings or facilities with large occupant loads.
- Ensures rapid evacuation and occupant safety under emergency conditions, aligning closely with both IBC and BSL.
- Automatic Door Allowances
- Global Provision: Automatic doors are permitted if equipped with fail-safe manual overrides that ensure doors can be opened manually during emergencies.
- Meets both IBC and BSL guidelines for functionality and emergency preparedness.
- Barrier-Free & Universal Design Compliance
- Universal accessibility and barrier-free design principles must be integrated following ADA/ICC A117.1 standards (IBC) and Japanese barrier-free design guidelines.
- Ensures comprehensive accessibility and inclusive usability for all occupants internationally.
These global door guidelines ensure consistent safety, accessibility, and regulatory compliance across diverse international environments.
TABLE 1006.3.2
MINIMUM NUMBER OF EXITS OR ACCESS TO EXITS PER STORY
| Occupant Load per Story | Minimum Number of Exits or Access to Exits from Story |
|---|---|
| 1–500 | 2 |
| 501–1,000 | 3 |
| More than 1,000 | 4 |
TABLE 1006.3.3(1)
STORIES WITH ONE EXIT OR ACCESS TO ONE EXIT FOR R-2 OCCUPANCIES
| Story | Occupancy | Maximum Number of Dwelling Units | Maximum Common Path of Egress Travel Distance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basement, first, second, or third story above grade plane | R-2¹ ² | 4 dwelling units | 125 feet |
| Fourth story above grade plane and higher | NP (Not Permitted) | NA (Not Applicable) | NA (Not Applicable) |
- For SI: 1 foot = 3048 mm.
- NP = Not Permitted.
- NA = Not Applicable.
- (a.) Buildings classified as Group R-2 equipped throughout with an automatic sprinkler system in accordance with Section 903.3.1.1 or 903.3.1.2 and provided with emergency escape and rescue openings in accordance with Section 1030.
- (b.) This table is used for R-2 occupancies consisting of dwelling units. For R-2 occupancies consisting of sleeping units, use Table 1006.3.3(2)
TABLE 1006.3.3(2)
STORIES WITH ONE EXIT OR ACCESS TO ONE EXIT FOR OTHER OCCUPANCIES
| Story | Occupancy | Maximum Occupant Load per Story | Maximum Common Path of Egress Travel Distance (feet) |
|---|---|---|---|
| First story above or below grade plane | A, B¹, E F¹, M, U | 49 | 75 |
| H-2, H-3 | 3 | 25 | |
| H-4, H-5, I, R-1, R-2² ³ | 10 | 75 | |
| S¹ ⁴ | 29 | 75 | |
| Second story above grade plane | B, F, M, S⁴ | 29 | 75 |
| Third story above grade plane and higher | NP (Not Permitted) | NA | NA |
- For SI: 1 foot = 304.8 mm.
- NP = Not Permitted.
- NA = Not Applicable.
- (a.) Buildings classified as Group R-2 equipped throughout with an automatic sprinkler system in accordance with Section 903.3.1.1 or 903.3.1.2 and provided
- with emergency escape and rescue openings in accordance with Section 1030.
- (b.) Group B, F and S occupancies in buildings equipped throughout with an automatic sprinkler system in accordance with Section 903.3.1.1 shall have a
- maximum exit access travel distance of 100 feet.
- (c.) This table is used for R-2 occupancies consisting of sleeping units. For R-2 occupancies consisting of dwelling units, use Table 1006.3.3(1).
- (d.) The length of exit access travel distance in a Group S-2 open parking garage shall be not more than 100 feet
