General Definition
- The minimum number of exits refers to the minimum required number of safe egress routes that must be provided in a building or space to ensure timely evacuation during emergencies.
- Building codes establish these requirements based on occupant load, building size, use classification, and fire safety considerations to prevent overcrowding and improve life safety.
- The Building Standard Law of Japan (BSL) Chapter 5 governs required exits, considering occupancy type, building size, fireproofing measures, and evacuation planning.
- The following is a comparative table integrating all aspects of means of exiting requirements for Group A-1 Occupancy under IBC Section 1006.3.2 and BSL Article 20 specific regulations:
| Means of Egress Aspect | IBC (International Building Code – USA) | BSL (Building Standards Law – Japan) |
| Occupancy Classification | Group A-1 (Assembly – Fixed seating for performance, e.g., theaters, concert halls) | Assembly Use Classification (劇場, 映画館, 集会所等) |
| Minimum Number of Exits | – 2 exits for occupant load ≤ 500 – 3 exits for 501-1,000 occupants – 4 exits for > 1,000 occupants (IBC 2018, Table 1006.3.2) | – 2 exits required for assembly use (BSL Article 20) – Additional exits required for large occupant loads based on layout and safety evaluation |
| Exit Width Requirements | – 0.3 inches (7.62 mm) per occupant for stairs – 0.2 inches (5.08 mm) per occupant for other egress components (IBC 2018, 1005.3.1, 1005.3.2) | – 90 cm (35.4 inches) minimum exit width (BSL Article 119) – 120 cm (47.2 inches) minimum for staircases in large assembly buildings |
| Corridor Width | – 44 inches (1118 mm) minimum (IBC 2018, 1020.2) | – 90 cm (35.4 inches) minimum (BSL Article 119) |
| Maximum Travel Distance to Exit | – 150 feet (45.72 m) (non-sprinklered) – 200 feet (60.96 m) (sprinklered) (IBC 2018, Table 1017.2) | – 30 meters (98.4 feet) (non-sprinklered) – 50 meters (164 feet) (sprinklered) (BSL Article 119) |
| Common Path of Travel | – 75 feet (22.86 m) (non-sprinklered) – 125 feet (38.1 m) (sprinklered) (IBC 2018, Table 1006.2.1) | – 20 meters (65.6 feet) (non-sprinklered) – 30 meters (98.4 feet) (sprinklered) (BSL Article 119) |
| Stairway Width | – 44 inches (1118 mm) minimum for occupant load > 50 (IBC 2018, 1011.2) | – 120 cm (47.2 inches) minimum for large assembly occupancies (BSL Article 119) |
| Minimum Ceiling Height | – 7 feet 6 inches (2286 mm) minimum (IBC 2018, 1003.2) | – 2.1 m to 2.3 m (6 feet 10 inches to 7 feet 6 inches) minimum depending on function (BSL Article 28) |
| Exit Signage & Emergency Lighting | – Required in all assembly occupancies (IBC 2018, 1013, 1008.3) | – Required in all assembly buildings (BSL Fire Code Enforcement Regulation Article 126) |
| Fire Resistance for Exit Enclosures | – 1-hour fire rating for ≤ 3 stories – 2-hour fire rating for > 3 stories (IBC 2018, 1023.2) | – 1-hour fire rating for ≤ 3 stories – 2-hour fire rating for > 3 stories (BSL Article 35, Fire Service Law) |
| Egress Doors Requirements | – Minimum 32 inches (813 mm) clear width – Must swing in the direction of egress travel for occupant load > 50 (IBC 2018, 1010.1.1, 1010.1.2.1) | – Minimum 80 cm (31.5 inches) clear width – Must swing outward for large occupancy (BSL Article 119, Fire Safety Regulations) |
- IBC strictly mandates a minimum number of exits based on occupant load, whereas BSL allows adjustments based on safety evaluations and layout.
- IBC allows longer travel distances (200 feet/60.96 m) in sprinklered buildings, whereas BSL has stricter limits (50 m/164 feet max).
- BSL enforces a minimum stair width of 120 cm (47.2 inches), which is wider than IBC’s 44-inch (1118 mm) minimum requirement.
- Both codes require emergency signage, fire-rated enclosures, and outward-swinging doors for large occupancies.
- BSL has a slightly lower ceiling height requirement (2.1 m vs. IBC’s 7 feet 6 inches).
Recommendations for Improving
- IBC (USA)
- Increase minimum stair width to 120 cm (47.2 inches) for better evacuation flow.
- Reduce maximum travel distances (especially for sprinklered buildings) to enhance fire safety.
- Mandate two exits for basement assembly spaces, even for small occupant loads.
- Increase egress door width to 900 mm (35 inches) for better accessibility.
- Require a 2-hour fire rating for all large assembly exit enclosures, regardless of height.
- BSL (Japan):
- Set a strict 4-exit requirement for >1,000 occupants (instead of layout-based flexibility).
- Allow slightly longer travel distances in fully fire-protected buildings.
- Increase stair width to 150 cm (59 inches) for assemblies over 2,000 occupants.
- Increase corridor width to 100 cm (39.4 inches) for smoother egress flow.
- Strengthen fire resistance requirements for high-occupancy buildings, even if low-rise.
Summary
- Align global standards for easier international compliance.
- Introduce performance-based egress design solutions.
- Encourage smart evacuation systems with AI-driven emergency signage.
- Strengthen universal design principles for improved accessibility.
Guidelines
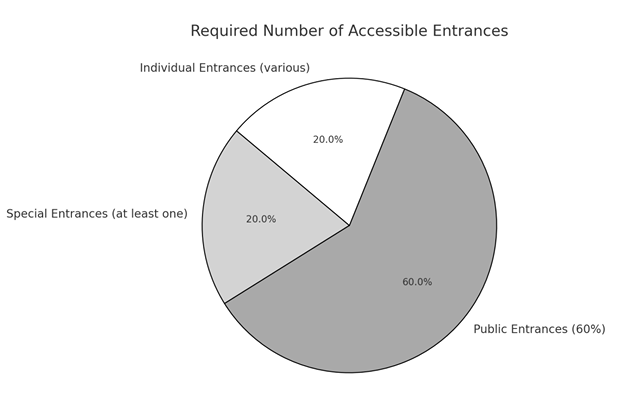
- Required Number of Accessible Entrance:
- Special entrances – at least one:
- Parking garages
- Tunnels
- Elevated walkways
- Restricted
- Inmates or detainees
- Public entrances:
- 60% of Building entrances
- At least one
- Individual entrance:
- Tenants’ spaces
- Accessible Group I
- Accessible Group R
- Special entrances – at least one: